MATLAB is a complete programming platform that includes a language, integrated development environment, and libraries. MATLAB stands for Matrix Laboratory and is aptly named for its facility in dealing with the matrix operations that form the foundation of much of scientific computing. In MATLAB terminology, libraries are known as toolboxes, and many different toolboxes are available to fit specific user requirements. We’re going to take a look at this valuable scientific programming tool and see who is using it and why they find it an attractive solution.
A Condensed History of MATLAB

The origins of MATLAB grew out of mathematical research done in the late 1960s through 1970 by J.H Wilkinson and his colleagues. Their work culminated in algorithms for the programming language Algol 60 that revolved around solving eigenvalue problems and matrix linear equations. Initiatives building on this work led to the development of high-quality mathematical software backed by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), which. made its debut in 1971 as EISPACK (Matrix Eigensystem Package). This was followed in 1975 by the creation of the Linear Equation package known as LINPACK.
The first MATLAB was an interactive matrix calculator that was developed as a programming exercise by Cleve Moler. It was designed to provide easier access to the LINPACK and EISPACK tools than that furnished by batch programming on a mainframe computer. From these humble beginnings, the concept was picked up by Jack Little and Steve Bangert leading to PC-MATLAB, which was introduced in 1984. It was designed to run on the new personal computers produced by IBM and was followed in 1985 by Pro-MATLAB, which ran on Unix workstations.
MATLAB has continued to evolve to satisfy the requirements of scientists and engineers. Here are some of the core components of the modern incarnation of the product.
Providing numerical solutions to ordinary differential equations (ODEs) is central to the functionality of MATLAB and its companion simulation product, Simulink. The original application only offered a single data type. All numbers were represented in the IEEE standard 754 double-precision floating-point format, stored in 64-bits of memory. Different data types aimed at providing more flexibility for MATLAB’s users have been added to the product over the years, resulting in a robust environment for mathematical computation.
- Single precision floating point numbers and integers were added in the early 2000s and enable the storage requirements of large arrays to be cut in half by using 32 bits of storage.
- Sparse matrices that represent matrices in a memory-efficient way were added in 1992. They only store nonzero values with pointers to rows and columns.
- Cell arrays and structures were implemented in 1996 and added increased functionality to the tool.
- Object-oriented capabilities were enhanced to MATLAB in 2008 to simplify programming tasks related to specialized data structures or functions that interact with specific types of data. It is the basis for the MATLAB graphics system.
MATLAB has progressed from a simple terminal application to a desktop solution in 2000. More recently, 2016 saw the Live Editor added. This feature lets users export MATLAB input, output, and graphics as an interactive document.
Toolboxes, which are known as libraries in other programming languages, are continually being developed and now number over 60 selections that address many aspects of mathematical computing. You can obtain toolboxes for such specialized applications as parallel computing, computational finance, and code generation.
The result of this innovation and continuous refinement is a full-featured mathematical programming platform that is widely used in universities, industry, and the scientific community.
How is MATLAB used?
So now that you have an overview of what MATLAB is, you may be wondering how it is used. The simple answer is that it has many applications in academia and a wide range of industries. Here are some of the most common ways you will find MATLAB being used today.
Over 6,500 universities worldwide make use of MATLAB and Simulink as teaching tools. The company offers campus-wide licenses, as well as product suites designed specifically for students. They also provide courseware and curriculum materials that facilitate its use. Students learn computational skills that prepare them for careers in diverse computing disciplines, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI). The widespread use of the tool in education produces thousands of new graduates every year who are well-versed in its application and can step right into jobs that demand its use on a professional level.
There is an incredible diversity in the way MATLAB is used in science and industry. What follows is just a small sampling of the ways the tool is being used by scientists and engineers across the globe.
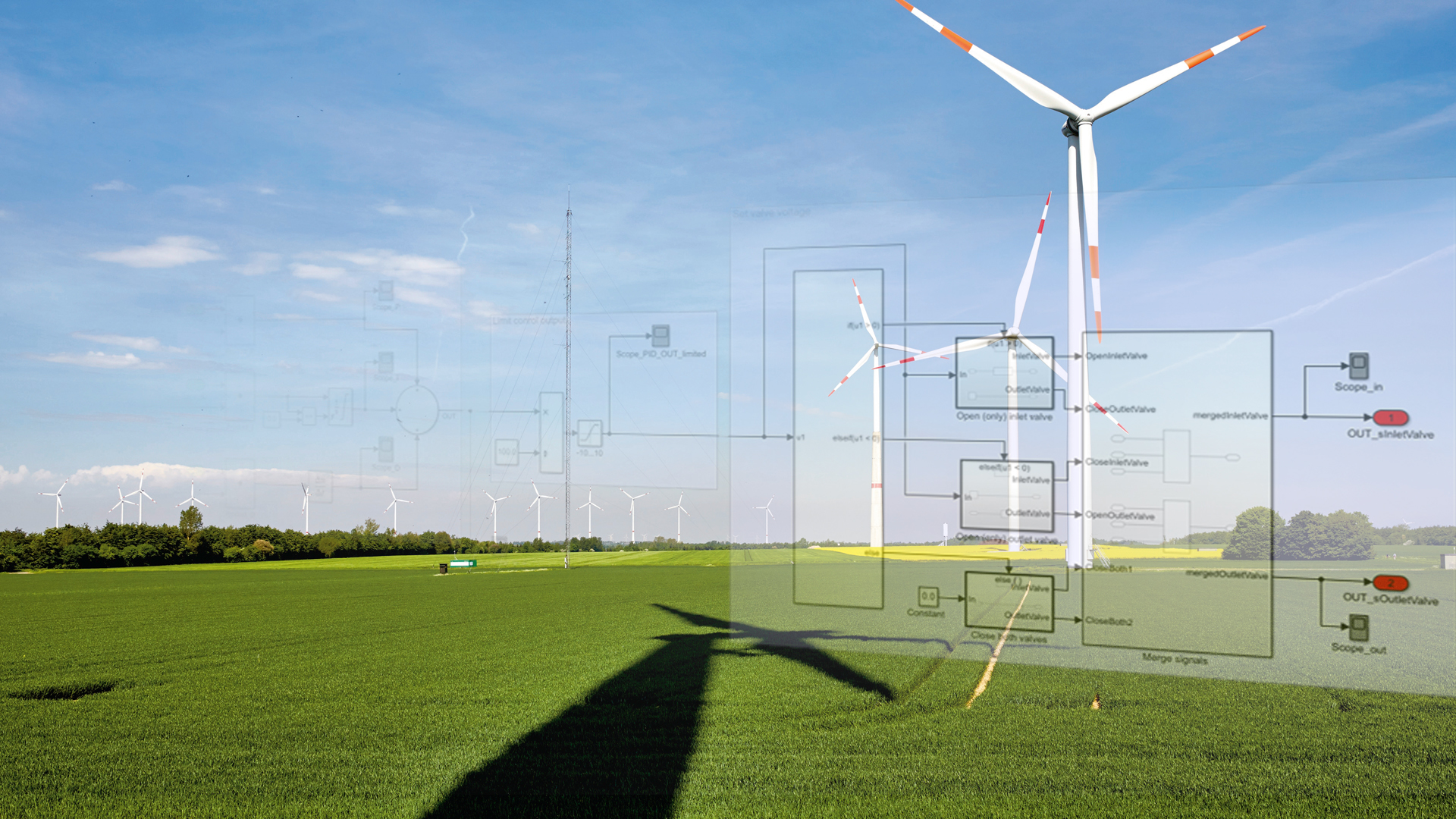
Real-time simulation and rapid prototyping are techniques that provide a fast and inexpensive method of verifying and evaluating designs for control and signal processing engineers. New designs can be tested in hardware in real-time and modifications can be made in minutes rather than days.
The mathematical modeling of complex systems is another area where MATLAB supplies enhanced capabilities to its users. It supports numeric and symbolic modeling, and paired with Simulink, creates a platform for the efficient development of embedded systems.
Physical modeling with the complementary Simscape product by Mathworks allows you to perform physical modeling that can be used throughout the development process. Combining the capabilities of MATLAB and Simulink enables deep learning and predictive maintenance to be incorporated into your models.
Taking advantage of the parallel computing capabilities of MATLAB speeds up data-intensive simulations and processing tasks. Make full use of multicore processors, GPUs, and cloud resources without making major changes to your workflows.
This is just a sampling of the ways MATLAB can be used to solve problems that require processing complex mathematical equations.
Examples of MATLAB in Action

A few concrete examples of MATLAB in action provide more insight into how the tool can benefit businesses in many different market sectors.
The utility and energy industry makes extensive use of modeling to ensure reliable power delivery to its customers. MATLAB and Simulink have been used to create a model of European power supply and demand to minimize costs and maintain optimal capacity across countries. Code can be directly implemented from its development platform to embedded systems for impressive gains in productivity.
Aerospace giant Airbus used Simulink to develop the fuel-management system on its Airbus A380. The complex system defines modes of operation on the ground and in flight and incorporates multiple thousands of states and transitions. The company saved months of development time and was able to handle additional complexity without the need to increase its staff.
The automotive industry is another area where MATLAB is accelerating the development of new technologies, such as Automated Driving and Advanced Driving Assistance Systems (ADAS). Functions such as control, planning, and perception can be simulated for testing, tuning, and integration purposes without the need for expensive prototype vehicles.
Why Should You Use MATLAB?
As can be seen from the collection of business and scientific disciplines making use of MATLAB, it provides extensive benefits that extend far beyond the classroom. So why should you consider MATLAB as a tool for your mathematical modeling and programming needs? Here are a few reasons to add MATLAB to your computing environment.
A large user base and extensive documentation make it easy to get up and running with MATLAB. Its almost universal use in education results in graduates who are well-versed in using the features of the tools to solve real-world problems. Companies are advised to employ young engineers with this skill set to take advantage of MATLAB’s capabilities for their business.
Code development is streamlined by the toolboxes made available to MATLAB users. The functionality provided by the toolboxes eliminates the need to write routines from scratch and lets developers try out ideas quickly and easily.
MATLAB code is concise with two lines of code being the equivalent of about 20 lines written in C++. This makes it much easier to understand the logic of code written by other programmers and facilitates sharing code among team members.
MATLAB is a mature programming platform that continues to add features and increase its functionality across the industrial, academic, and scientific worlds. It just might be the right time for you to see how it can be used to solve complex mathematical problems plaguing your company.